December 25th, 2025
How to Use Feedback Data for Product Validation
Validate product ideas with customer feedback: set testable hypotheses, run landing-page and fake-checkout tests, analyze behavior, then build, pivot, or stop.
Warren Day
Building products without user feedback is risky. Many teams rely on guesswork, but structured feedback data helps answer three key questions:
- Do users want this?
- Can they use it?
- Can we build it?
Using both numbers (click-through rates) and user insights (interviews), you can validate ideas early, avoiding costly mistakes like Facebook Home's failure in 2013. Tools like LaunchSignal simplify this process by testing demand using landing pages, surveys, and fake checkouts before development begins.
The process involves:
- Setting clear goals and measurable hypotheses.
- Collecting feedback through surveys, landing pages, and real user actions (e.g., pre-orders).
- Analyzing data to prioritize features and identify real user needs.
- Making decisions based on evidence - proceed, pivot, or stop.
- Creating a continuous feedback loop to improve over time.
Using structured methods ensures you're solving the right problems for your audience while saving time and resources.
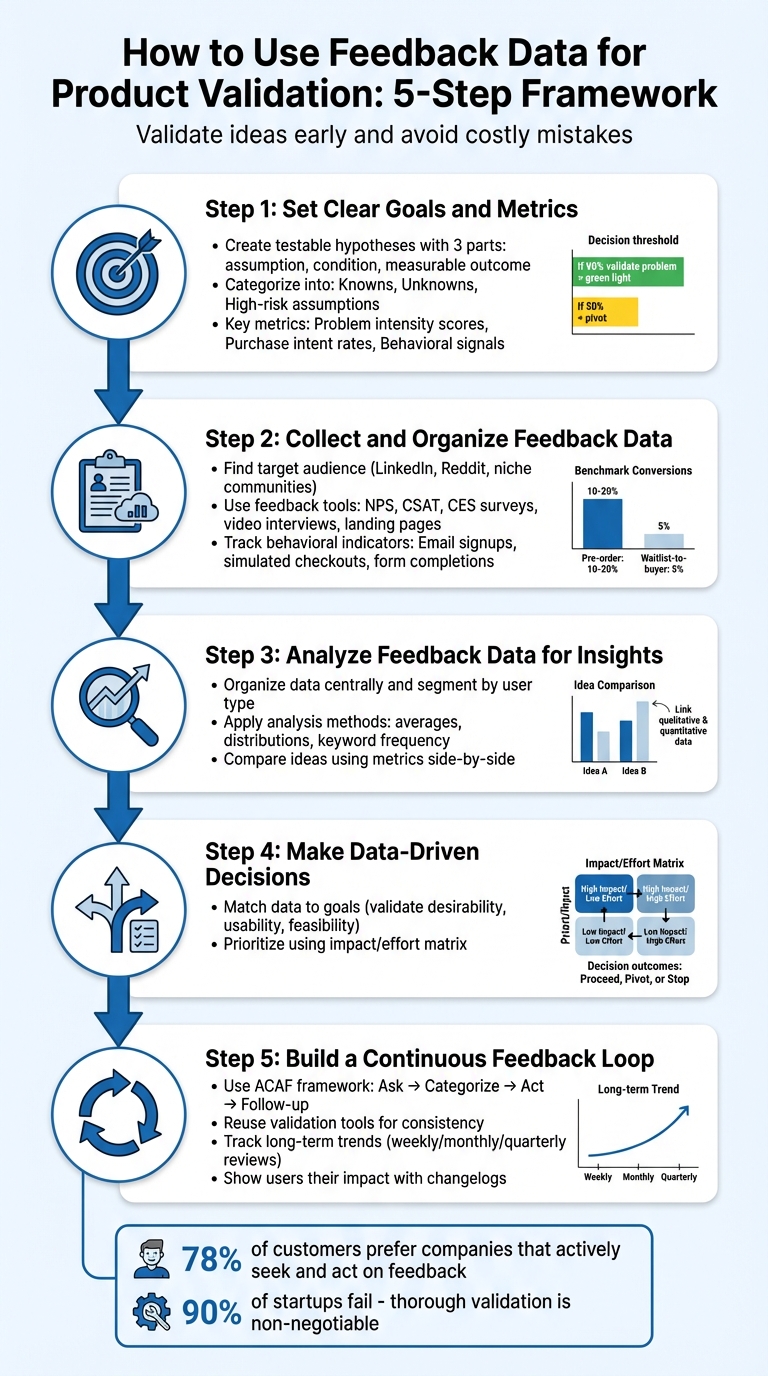
5-Step Product Validation Process Using Feedback Data
Step 1: Set Clear Goals and Metrics
Before diving into gathering feedback, it’s crucial to define your testing objectives and success metrics. Without this clarity, you risk being overwhelmed by irrelevant data. Think of it this way: an idea like "shorten the checkout process" is vague, but turning it into a hypothesis such as "if we reduce checkout to two steps, we will increase completed orders by 15%" makes it specific and testable. Start by breaking your goals into clear, actionable hypotheses.
Create Testable Hypotheses
A strong hypothesis includes three parts: an assumption, a condition, and a measurable outcome. One helpful framework is: "[Client] will spend [amount] to purchase [product] to solve [problem]." This approach forces you to clearly define your audience, price point, and the problem you aim to address.
Next, categorize your assumptions into three groups:
- Knowns: Facts you’ve already confirmed.
- Unknowns: Areas where you need more information.
- High-risk assumptions: Beliefs that, if proven wrong, could derail your entire idea.
Focus first on testing high-risk assumptions. For instance, if your hypothesis hinges on customers being willing to pay a specific price, validating this early is critical. Ignoring such risks could jeopardize your entire plan.
Choose Key Success Metrics
Once your hypotheses are ready, identify metrics that directly measure the outcomes you expect. For product validation, consider metrics like:
- Problem intensity scores: How severely users feel the pain point you’re addressing.
- Purchase intent rates: The percentage of users willing to buy.
- Behavioral signals: Actions like email sign-ups or simulated purchases.
For landing page experiments, metrics such as email sign-up rates and click-through rates on calls-to-action (CTAs) can provide a reliable gauge of interest. Testing willingness to pay? Go beyond surveys. Real monetary commitments, like pre-orders or crowdfunding, offer stronger validation. A great example: In 2012, Oculus demonstrated demand for its VR headset by raising $250,000 within hours on Kickstarter. This showed that actual financial backing speaks louder than verbal interest.
Set Decision Thresholds
Before testing, establish clear criteria for whether to proceed, refine, or abandon your hypothesis. For example: "If I approach 15 target users and don’t achieve at least 3 conversions, I’ll revisit the core hypothesis". Similarly, if 90% of survey respondents validate your problem, that’s a green light. But if only 50% do, you’ll likely need a major pivot.
Don’t forget to factor in financial viability when setting your thresholds. Ensure your customer acquisition cost (CAC) will be lower than the revenue you expect from each customer. Remember, about 90% of startups fail, so thorough validation in the early stages is non-negotiable. As Eric Ries wisely said:
"The pivotal question is not whether a product can be built, but whether it should be built".
Step 2: Collect and Organize Feedback Data
After setting your goals and metrics, the next step is to gather feedback from users. Focus on what people do, not just what they say. Behavioral signals - real actions - are often more telling than opinions. As Nimi Kular, co-founder of Jaswant's Kitchen, puts it:
"Market evaluation, surveys, and feedback from friends and family can point you in the right direction, but money is the only thing that can validate a product".
The key is identifying the audience whose behavior will give you the clearest insights.
Find Your Target Audience
Start by figuring out where your potential customers already hang out. If you're aiming at professionals, LinkedIn groups or niche Slack communities are great options. For consumer products, platforms like Reddit, Facebook groups, or even Instagram can connect you with early testers. Take Popl, for example - a digital business card company. In 2020, they discovered through customer interviews that their product was more valuable for professional use than casual scenarios. This realization led co-founder Nick Eischens to pivot toward a professional model, which boosted premium subscriptions.
The takeaway? Avoid relying on friends and family for feedback. Instead, recruit testers who genuinely match your buyer persona - considering factors like age, income, and shopping habits. This ensures your feedback aligns directly with the goals you set in Step 1.
Use Feedback Collection Tools
To gather meaningful data, use a mix of tools for both numbers and insights. Surveys like Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), and Customer Effort Score (CES) provide measurable data on customer sentiment and pain points. For more detailed insights, try one-on-one video interviews to explore the "why" behind user actions.
Landing pages are another powerful tool for early validation. Platforms like LaunchSignal let you create simple landing pages with features like email capture, questionnaires, and even fake checkout buttons - no coding required. These "fake door" tests measure real interest before you invest in building a product. Keep an eye on engagement rates: a good validation benchmark is 10% to 20% pre-order conversions, while waitlist-to-buyer conversion rates should hover around 5%. Once you’ve collected this data, analyze user actions to understand their true intent.
Track Behavioral Indicators
Focus on what users do, not just what they say. Actions like email signups, simulated checkouts, and form completions are much better indicators of genuine interest than survey responses. For example, Jacob Winter, founder of Mush Studios, validated his "Blot Rug" design by tracking TikTok engagement. The irregular-shaped rug went viral, racking up 23 million views in its first year, proving its appeal before any major investment.
Pay attention to subtle behavioral cues too, like "hover-but-not-click" rates or drop-off points, which can reveal where users experience hesitation. The ultimate validation? When users take real action - especially when it involves spending money.
Step 3: Analyze Feedback Data for Insights
Transforming raw feedback into meaningful insights is what separates informed product validation from random guesswork. Anna Schmunk from LogRocket captures this perfectly:
"Customer feedback analysis is the art and science of taking disparate data sources and feedback points from your customers and synthesizing them into clear, concise insights".
The aim? Spot patterns that confirm whether your product idea solves a real problem.
Organize Your Data
Start by gathering all feedback in one place - emails, social media mentions, support tickets, and survey responses. Keeping everything centralized ensures no valuable insight slips through the cracks. Then, segment this data by factors like user type, date, or product feature. For instance, feedback from paying customers might carry more weight than feedback from free trial users.
To dig deeper, link each piece of feedback to customer details such as spending level, account age, or usage frequency. This helps you prioritize input from your most important user segments. Categorize feedback into groups like bug reports, feature requests, or usability issues, and tag it by urgency. Let themes naturally emerge from the data instead of forcing predefined categories - this reduces the risk of confirmation bias.
Apply Basic Analysis Methods
Use straightforward metrics like averages, distributions, and frequencies to evaluate key success indicators. For example, a solid Net Promoter Score (NPS) based on a substantial number of responses can provide a reliable benchmark. Watch for frequently mentioned keywords - words like "confusing" or "expensive" can highlight critical problem areas.
For qualitative data, organize open-ended responses into themes such as pricing concerns, usability challenges, or feature gaps. Focus on a few major themes to avoid drowning in data. Use bar charts with percentages to present findings clearly - word clouds often lack the necessary context. While quantitative data shows you what's happening, qualitative insights help explain why users respond the way they do. Compare these findings across your product ideas to identify trends.
Compare Ideas Using Metrics
When testing multiple product concepts, side-by-side comparisons can reveal which one resonates most with your audience. Track metrics like email signup rates, fake checkout conversions, or common objections. For instance, if one concept results in higher email signups, it likely connects better with your target market.
Platforms like LaunchSignal simplify this process by allowing you to test multiple validation pages simultaneously. Use their analytics dashboard to compare metrics in real time. Pay close attention to recurring complaints (friction clusters) about specific workflows - these often highlight pain points users are eager to have addressed. When qualitative feedback aligns with hard data, it’s a strong indicator that your product idea is hitting the mark.
sbb-itb-9a9c51d
Step 4: Make Data-Driven Decisions
Once you've analyzed your feedback, the next step is to decide whether to move forward, pivot, or stop entirely - using the evidence you've gathered to guide your choice.
Match Data to Your Goals
Now that you’ve collected insights, it’s time to turn that data into actionable steps. Start by comparing the feedback against the hypotheses and success metrics you established earlier. For example, if your goal was a 5% conversion rate for email signups and you’re seeing 7%, that’s a strong validation. But if you’re only at 2%, it might be time to rethink your approach.
Andrei Beno, Sr. Director of Product at Contentsquare, explains this balance perfectly:
"Validation is most useful for assessing a new feature or product... Experimentation is most useful to assess iterations and improvements to a feature or product once it's already in use".
To validate your idea, ensure it meets three key criteria: desirability, usability, and feasibility. For instance, high email signup rates suggest desirability, but if users report confusion about your product, you may have a usability issue to resolve before moving forward. This process ties back to the success metrics you outlined earlier.
Also, confirm that your product delivers value that matches its price point. Nick Eischens, COO and co-founder at Popl, shared how customer feedback shaped their direction:
"Our conversations with customers helped us identify their main problem and shift our focus to a professional use case".
Prioritize Key Issues
Not all feedback carries the same weight. Start by organizing feedback into categories - such as bugs, feature requests, or user interface (UI) issues - to ensure critical problems, like security flaws or app-breaking bugs, are addressed first, while less urgent updates can wait.
To better understand the impact of feedback, turn qualitative themes into quantitative data. For example, if 40% of respondents mention pricing concerns but only 8% bring up color scheme preferences, you know where to focus your efforts. Using percentages rather than raw numbers helps you see the bigger picture.
It’s also smart to link feedback to customer metadata. Pay closer attention to input from high-value customers or core user groups, rather than free trial users who may not align with your ideal audience. A priority matrix can help you sort tasks into four categories:
- High Impact / Low Effort: Quick wins that are easy to implement.
- High Impact / High Effort: Larger projects that need careful planning.
- Low Impact / Low Effort: Minor improvements to consider if resources allow.
- Low Impact / High Effort: Initiatives that are usually not worth pursuing.
For example, if you're testing multiple ideas using LaunchSignal's analytics, compare metrics like fake checkout conversion rates across different validation pages. If one idea achieves a 12% conversion rate while another only reaches 3%, the data clearly points to the stronger option. These priorities will guide your next steps and keep your decisions focused.
Document Your Decisions
Transparency is key to building trust, especially since 55% of U.S. consumers doubt that businesses act on feedback. Documenting your process - what you learned, the decisions you made, and why - helps address this skepticism. It also ensures that every decision informs future validation cycles.
Create a central feedback repository, like a spreadsheet or database, to log all feedback, customer details, and its source. Use tags to categorize entries by urgency and type, so you can identify patterns and justify your decisions to stakeholders.
For each validation cycle, record the hypothesis you tested, the data you gathered, the insights you gained, and the actions you took - whether that’s moving forward, pivoting, or stopping. This documentation keeps your team aligned and supports future iterations.
Taking it a step further, public roadmaps can show customers that their voices are heard. As Petra Odak, CMO at Better Proposals, explains:
"If a feature is necessary, we'll have quite a few people asking for it or talking about it".
Sharing your roadmap signals that you’re listening, which resonates with the 78% of U.S. customers who prefer companies that actively seek and act on feedback.
Step 5: Build a Continuous Feedback Loop
Great products don’t just happen - they grow and improve through constant feedback. Think of feedback as an ongoing conversation with your users, not a one-off event. This mindset is what keeps products thriving while others fall behind.
Set Up Regular Feedback Cycles
Make feedback a regular part of your process by scheduling validation after every iteration. The ACAF framework is a handy guide for this: Ask (gather feedback), Categorize (group feedback into themes), Act (implement changes), and Follow-up (close the loop with users). To make this seamless, dedicate a portion of each development sprint to addressing user-reported issues. For example, setting aside time in every sprint specifically for feedback ensures that user insights are consistently turned into action.
Don’t rely solely on one method to gather input. Automate tracking for metrics like usage, errors, and performance to collect quantitative data. Pair this with qualitative methods - like weekly user interviews or monthly surveys - to understand the "why" behind the numbers.
Reuse Validation Tools
Streamline your process by reusing validation workflows for new iterations or product ideas. Tools like LaunchSignal make this easy. For instance, if you’ve already created a validation page with email capture and questionnaires, you can quickly adapt it for future experiments.
Reusing these tools also ensures consistency. Tracking metrics like conversion rates across different iterations can give you clear evidence of progress. By sticking to proven workflows, you save time and create a solid foundation for long-term tracking.
Track Long-Term Trends
Keep an eye on the big picture by regularly reviewing key metrics and feedback themes. Whether you choose weekly, monthly, or quarterly reviews, these check-ins help you identify emerging issues and new opportunities.
Organize qualitative data with keyword and sentiment tagging to spot trends in areas like "pricing", "usability", or "bugs." This makes it easier to see which themes are gaining or losing importance over time. Then, cross-check these insights with behavioral data - such as usage analytics or churn rates - to confirm whether reported issues match real-world performance.
Finally, show your users that their feedback matters. Use changelogs or "user-requested" tags in release notes to highlight updates inspired by their input. This is especially important because only 55% of U.S. consumers believe businesses act on their feedback. When you demonstrate that you’re listening, you not only build trust but also encourage users to keep sharing their thoughts. Over time, this feedback loop strengthens your product’s connection to user needs and turns customers into loyal advocates.
Conclusion
Achieving effective product validation starts with clear goals, structured data collection, and thorough analysis. The key is to ask the right questions and align your efforts with what users truly need. For example, setting measurable success metrics - like aiming for a conversion rate above 5% or a customer satisfaction score exceeding 4.5 - provides an unbiased foundation for decision-making. These benchmarks ensure you're not relying solely on internal opinions but instead focusing on actual user behavior.
The process revolves around gathering data, analyzing it, and taking decisive action. By combining quantitative data (like metrics and analytics) with qualitative insights (like user feedback), you can identify critical issues and prioritize meaningful changes.
Tools like LaunchSignal make this workflow more seamless. With LaunchSignal, you can validate ideas before writing any code. Test demand using landing pages with email capture forms, assess willingness to pay with simulated checkouts, and compare concepts side-by-side through its analytics dashboard. Plus, you can export the data to guide your decisions - all without needing design or coding expertise. These tools help extend the feedback loop across every stage of development, reinforcing the strategic process.
As Jesse Sumrak from LaunchDarkly aptly states:
"Software isn't finished when it ships. That's just the beginning of product development".
To maximize impact, set up regular feedback cycles, monitor trends over time, and show users how their input has shaped your product. This approach not only minimizes wasted development time but also strengthens customer loyalty. By integrating these practices, you can continuously refine your product strategy and keep your users at the center of your decisions.
FAQs
How can I effectively validate my product idea using customer feedback?
To ensure your product idea has potential, start by defining clear assumptions about your target audience. Pinpoint their challenges, understand their needs, and assess their willingness to pay for a solution. Build detailed customer personas to dive deeper into their demographics, motivations, and buying habits. Depending on where you are in the development process, select an appropriate feedback method. For early-stage ideas, quick surveys or landing page sign-ups work well. If you’re further along, prototypes can be tested using in-app surveys or even "fake checkout" experiments to gauge interest.
Collect enough responses to spot patterns and confirm the authenticity of the feedback. Break your data into segments - such as user types, sentiment, or specific feature requests - and look for recurring themes that suggest strong demand. With these insights in hand, test multiple ideas using low-cost experiments. Platforms like LaunchSignal can simplify this process by letting you create landing pages, capture user interest with forms or fake checkouts, and analyze metrics like conversion rates or cost-per-lead to identify the most promising directions.
Remember, validation doesn’t stop at launch. Continuously monitor how users engage with your product, gather feedback, and adjust your roadmap to focus on what delivers the most value. By blending data-driven experiments with ongoing feedback, you can create a product that meets real customer needs while keeping risks and expenses in check.
What mistakes should I avoid when gathering feedback to validate a product idea?
When gathering feedback to validate a product idea, it's essential to sidestep common mistakes that can compromise the quality of your data. Here are some pitfalls you’ll want to avoid:
- Overloading your audience: Sending out too many surveys or designing ones that are overly long can discourage participation or result in incomplete answers.
- Using unclear or biased questions: Ambiguous or leading questions can distort responses and fail to reveal what users truly need or think.
- Reaching the wrong audience: Feedback from people who don’t understand your concept won’t provide insights that are relevant or helpful.
- Lacking clear objectives: Without well-defined goals, it becomes difficult to link feedback to specific hypotheses or actionable takeaways.
- Skipping segmentation: If you don’t organize responses by categories or priorities, identifying meaningful patterns becomes a challenge.
- Failing to act on feedback: Gathering data without using it - or making decisions without confirming its accuracy - wastes time and resources.
LaunchSignal makes this process smoother by offering tools designed to collect focused, reliable feedback. With features like pre-built survey templates, precise audience targeting, and integrated analytics, you can confidently gather insights and make informed, data-backed decisions.
How can I prioritize customer feedback from different user groups?
To make the most of customer feedback, start by organizing it based on user groups like new users, power users, or enterprise customers. Tagging feedback this way allows you to filter and analyze it by segment, making it easier to spot trends and address specific needs.
Next, evaluate feedback using three main factors:
- Segment size: Larger groups tend to have a greater overall impact.
- Strategic importance: For instance, feedback from high-value customers might carry more weight.
- Impact of the request: Consider how severe the issue is or the potential benefit of addressing it.
By assigning scores to these factors, you can calculate a total priority score to rank feedback and focus on what matters most.
Be cautious of biases, such as a vocal minority overshadowing broader trends. Instead, look for patterns that span multiple user groups. For example, if both "new users" and "power users" are asking for the same feature, it likely deserves more attention. Tools like LaunchSignal can help you track user activity - like email sign-ups or survey responses - to quickly identify trends and validate ideas.
Once you've identified high-priority feedback, review it with your team and stakeholders to ensure it aligns with your overall objectives. Don’t forget to revisit and refine your scoring process over time to keep up with shifting customer needs and market dynamics.
Start validating ideas in minutes not days
Create high-converting landing pages. Test with real users. Get purchase signals. Know what to build next.
Visit LaunchSignal